Introduction to Cloud Computing
Among the many technological developments of the modern era, cloud computing is particularly important. In its simplest form, cloud computing is the internet-based delivery of diverse computing services. Many assets are included in these services, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and more. The fundamental idea is to provide users with remote access to and control over data and applications, free from the limitations of physical infrastructure.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition and basic concept
- Types
- Public cloud
- Private cloud
- Hybrid cloud
- Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Cost-effectiveness
- Scalability
- Flexibility
- Challenges of Cloud Computing
- Security concerns
- Data privacy issues
- Downtime risks
- Applications of Cloud Computing
- Business operations
- Data storage and backup
- Software development
- Popular Cloud Service Providers
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Trends in Cloud Computing
- Edge computing
- Serverless computing
- Multi-cloud strategies
- Future Outlook of Cloud Computing
- Growth projections
- Technological advancements
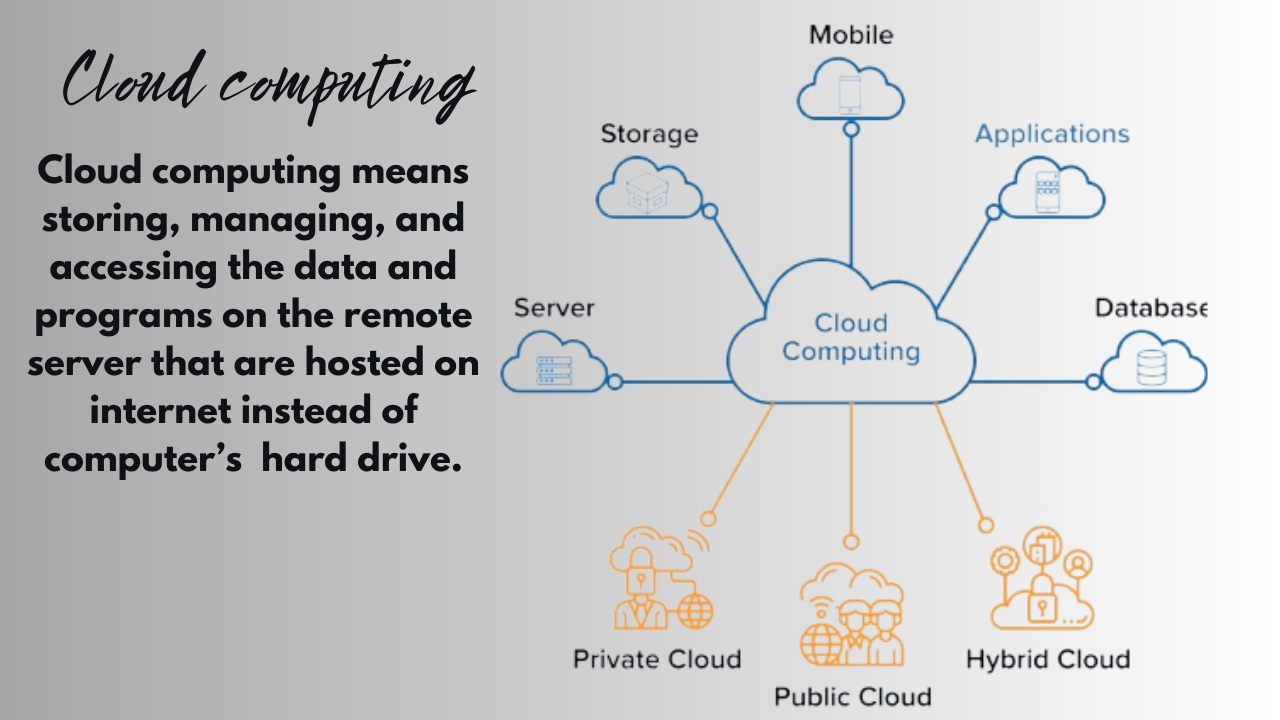
What is Cloud computing?
The utilization of hosted services, including servers, databases, networking, software, and data storage via the Internet, is known as cloud computing. Since, the advent of cloud computing, the number of cloud-based IT services and apps has increased dramatically and is still growing worldwide.
Types of Cloud Computing
Public Cloud: A public cloud is a cloud computing architecture in which third-party providers offer infrastructure and services to the larger public online. The cloud provider hosts and maintains these services; they are also in charge of updating and upgrading the system, maintaining security, and maintaining infrastructure. Pay-as-you-go public cloud services enable users to access computer resources like servers, storage, and apps in accordance with their demands without having to make an initial investment in hardware or infrastructure.
Private Cloud: A private cloud is a cloud computing environment that is only available to one business or entity, offering resources and services related to computing. In contrast to public clouds, private clouds offer more control, flexibility, and security and are usually hosted on-site or by a third-party provider. Because they provide more control over data privacy, security procedures, and resource allocation, private clouds are perfect for enterprises with particular safety, regulatory, or performance requirements. However, compared to public clouds, private clouds could need more initial funding and continuous maintenance.
Hybrid Cloud
By combining aspects of the public and private cloud models, a hybrid cloud enables businesses to take advantage of both environments’ advantages. Organizations can flexibly move workloads between public and private clouds in hybrid setups, optimizing for cost, performance, and security. This allows them to leverage the scalability and affordability of public clouds while controlling sensitive data and adapting resources as needed. Hybrid clouds suit businesses with varied workloads, regulatory constraints, or legacy systems.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is changing the way people and organizations manage and access data and apps, and it has many advantages for both. Among the principal benefits are:
Cost-effectiveness: Because cloud services are usually provided on an ongoing basis, cloud computing eliminates the need for an upfront investment in hardware, infrastructure, and maintenance. Organizations can scale resources up or down as needed with this affordable pricing approach, which lowers overall IT costs.
Scalability: Cloud computing enables businesses to quickly and easily scale resources in response to changing demands by giving them on-demand access to computing resources like servers, storage, and apps. Businesses can satisfy expanding demands because of this scalability, which eliminates the need for new infrastructure or technology.
Flexibility: With cloud computing, customers can use any device with an internet connection to access data and applications from anywhere. This adaptability enables firms to adjust to shifting work environments and client expectations by enabling remote collaboration, mobile access, and increased productivity.
Reliability: To guarantee high availability and dependability, cloud service providers make significant investments in infrastructure and security protocols. This implies that customers will always have access to data and apps hosted in the cloud because they are redundant, backed up, and safeguarded from hardware failures.
Security: In contrast to popular belief, cloud computing companies put strong security measures in place to guard against cyber attacks, illegal access, and data breaches. Access restrictions, identity management, encryption, and frequent security audits are some of the cloud security elements that guarantee data security and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Challenges of Cloud Computing
While cloud computing offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges and concerns that organizations must address:
Security concerns: There are security hazards when storing confidential information and software on remote computers run by other companies. Concerns among organizations include data breaches, unauthorized access, and the compromise of sensitive information. Cloud service providers put strong security measures in place, such as encryption, access controls, and frequent security audits, to allay these worries. To safeguard their data in the cloud, users must, therefore, also put additional security measures and best practices into place.
Data Privacy Issues: Cloud computing raises concerns over data control, ownership, and jurisdiction. Regulations like the CCPA and GDPR limit data collection and storage. To ensure data privacy, organizations must evaluate cloud providers, ensure compliance with laws, and use encryption and access controls.
Risks Associated with Downtime:
Businesses that use cloud computing services have a big risk of experiencing downtime. Businesses should have strong backup and disaster recovery plans in place, which include redundant systems, data replication, and failure procedures, to reduce downtime risk. Downtime can cause financial losses, ruin reputations, and interfere with business operations. Cloud computing is crucial for modern technology, with applications across various industries. Our platform provides access to various processes, such as email and document management, allowing seamless communication and collaboration.
Application of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has become an integral part of modern technology, offering a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some of the key areas where cloud computing is making a significant impact:
Business Operations: Cloud computing enables businesses to streamline their operations by providing access to a suite of productivity tools, such as email, document management, and collaboration software. These cloud-based applications allow employees to work from anywhere, at any time, using any device with an internet connection. Additionally, cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) systems help businesses manage customer data, track sales leads, and streamline marketing efforts.
Data Backup and Storage: Cloud computing offers an affordable and scalable solution for data backup and storage. Businesses may safely store and access massive amounts of data by utilizing cloud storage services rather than spending a lot of money on on-premises storage hardware. Cloud storage companies guarantee data availability and integrity by providing features like encryption, redundancy, and data replication.
Software Development: Cloud computing accelerates software development by providing developers with a range of tools and resources. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform offer code collections, testing environments, and installation tools, enabling rapid and efficient application creation, testing, and launch. Cloud-based DevOps solutions automate the software development lifecycle, enabling continuous integration and delivery.
Big Data Analytics:
Cloud computing provides a scalable and cost-effective platform for processing and analyzing large volumes of data. Services for cloud-based analytics, such as Microsoft Azure Analytics, Google Big Query format, and Amazon Redshift, provide strong tools and algorithms for deriving insights from data. By using these services, companies can obtain useful information about consumer behavior, industry trends, and internal business processes, which improves decision-making and gives them a competitive edge.
IoT (Internet of Things): Cloud computing plays a crucial role in powering IoT devices and applications. Cloud-based IoT platforms provide the infrastructure and services needed to collect, store, and analyze data from connected devices. By leveraging cloud computing, businesses can harness the power of IoT to improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation.
Machine learning and AI: Cloud computing enables the development and deployment of machine learning and AI applications. Platforms like AWS, Google Cloud AI, and Azure provide pre-built algorithms and tools for training and deploying models. These platforms allow businesses to utilize machine learning and AI to automate processes, gain insights, and make predictions.
Popular Cloud Service Providers
Here are some of the most popular cloud service providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS leads in cloud services, offering computing power, storage, databases, machine learning, analytics, and more. With a global network and diverse services, it serves businesses of all sizes and industries.
2. Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure makes deploying apps and services via Microsoft data centers easier. It offers virtual machines, databases, AI, IoT, and DevOps tools in the cloud.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
GCP is Google’s cloud computing platform, offering a suite of cloud services including storage, databases, machine learning, and analytics. GCP empowers businesses with innovative and sustainable tools for efficient application and service development, deployment, and scaling.
4. IBM Cloud: IBM is a platform for cloud computing that it offers. It offers various services for creating, implementing, and monitoring services and applications in public, private, and hybrid cloud environments. With a strong focus on security, compliance, and industry-specific solutions, IBM Cloud caters to businesses with diverse needs and requirements.
5. Oracle Cloud: Oracle Cloud is Oracle’s cloud computing platform, offering a comprehensive suite of cloud services, including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). With a focus on enterprise-grade performance, security, and reliability, Oracle Cloud provides businesses with the tools and resources needed to innovate and grow.
Trends in Cloud Computing
Here are some of the key trends shaping the future of cloud computing:
- Edge Computing: Many organizations are seeking greater agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness for their operations. Serverless platforms scale resources automatically, cutting planning needs and reducing operational work. Plus, more organizations use multi-cloud strategies to leverage various providers’ strengths and avoid vendor lock-in. This approach involves distributing operations across different cloud platforms.
2. Serverless Computing: Serverless computing, also known as function as a service (FaaS), is revolutionizing the way developers build and deploy applications. With serverless computing, developers can focus on writing code without managing infrastructure, allowing for greater agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Serverless platforms automatically scale resources based on demand, eliminating the need for capacity planning and reducing operational overhead.
3. Multi-cloud Strategies: Organizations are increasingly adopting multi-cloud strategies to leverage the strengths of multiple cloud providers and avoid vendor lock-in. By distributing workloads across multiple cloud environments, organizations can optimize performance, reduce costs, and mitigate risks. Multi-cloud architectures also provide flexibility and redundancy, ensuring high availability and reliability for mission-critical applications.
4. Hybrid Cloud Adoption:
As businesses look to strike a balance between the advantages of public cloud services and the control and security of private cloud environments, hybrid cloud adoption is growing. Cloud-native development practices enable organizations to rapidly develop, deploy, and scale applications. This leads to accelerated innovation, improved agility, and reduced time-to-market. Cloud computing is driving the adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies as they are easily accessible on the cloud.
5. Cloud-native Development:
Enterprise adoption of microservices, containers, and container management platforms such as Kubernetes drives the surge in cloud-native development. These applications, built to operate in the cloud, utilize scalable and resilient architectures for swift development, deployment, and scaling. By adopting cloud-native development practices, organizations can accelerate innovation, improve agility, and reduce time to market.
6. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Cloud computing is facilitating the adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies by providing the computational resources and infrastructure needed to develop and deploy AI/ML applications at scale. Cloud-based AI/ML platforms offer pre-built models, tools, and APIs for training and inference, enabling organizations to derive insights, automate processes, and make predictions from their data.
7. Data Management and Analytics: Cloud computing is transforming the way organizations manage and analyze data, with a growing emphasis on cloud-based data management and analytics platforms. Cloud-based data lakes and analytics services offer scalable and cost-effective solutions for storing, processing, and analyzing large volumes of data. These platforms enable organizations to gain valuable insights, drive data-driven decision-making, and unlock new business opportunities.
Future Outlook of Cloud Computing
The future of cloud computing appears promising, with ongoing advancements and evolving trends shaping the industry’s trajectory. Here’s an overview of what to expect in the coming years:
- Continued Growth: The global cloud computing market is poised for sustained growth as businesses increasingly embrace cloud solutions to drive innovation and agility. Forecasts indicate that the market will continue to expand, with cloud adoption becoming mainstream across industries and sectors.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing is set to become more prevalent as organizations seek to process data closer to its source, reducing latency and improving performance for latency-sensitive applications. Edge computing will enable new use cases in areas such as IoT, autonomous vehicles, and real-time analytics.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: Hybrid and multi-cloud approaches will gain traction as organizations seek to optimize their cloud deployments for performance, scalability, and cost-efficiency. By leveraging a mix of public, private, and edge clouds, organizations can achieve greater flexibility, resilience, and control over their IT environments.
- Security and Compliance: Security and compliance will remain top priorities in cloud computing. As data breaches and cyber threats continue to pose risks, organizations will invest in robust security measures and compliance frameworks to protect sensitive data and ensure regulatory compliance. Cloud providers will enhance their security offerings to address emerging threats and evolving regulatory requirements.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: AI and machine learning technologies will play a significant role in shaping the future of cloud computing. Cloud providers will integrate AI and ML capabilities into their services, enabling organizations to derive actionable insights, automate processes, and drive innovation at scale.
.
nobis nobis ab quae ab aut ea fugiat earum voluptatem consequuntur fugiat alias qui est fugit. sed quia et numquam ipsam commodi. delectus quas et suscipit est praesentium cumque sed minima dolores earum id animi rem et dignissimos et.
What’s the most reliable payment gateway for high risk businesses?